Madagascar
Madagascar is an island nation in the western Indian Ocean and the world’s fourth-largest island, stretching about 1,600 km north–south and 580 km east–west. A global biodiversity hotspot, it hosts roughly 5% of the world’s biodiversity. The economy relies heavily on natural resources, underscoring the central role of Malagasy biodiversity across the country’s ecology, economy, society, and culture. Yet the ecosystem functions and services that support well-being and development are threatened by deforestation, habitat degradation, land and coastal erosion, rapid depletion of natural resources, and the loss of endemic species. Despite conservation efforts, these pressures remain concerning, compounded by historically low investment in biodiversity.
In 2019, Madagascar joined UNDP’s Biodiversity Finance Initiative (BIOFIN) to develop a Biodiversity Finance Plan (BFP). The methodological phase concluded in December 2022 with the BFP finalized and validated by the National Steering Committee.
Since January 2023, the programme has entered its second phase, implementing priority financing mechanisms identified in the BFP, including:
- Results-based budgeting
- Protected area financing
- Forestry-sector taxes, fees, and royalties
- Sustainable blue-economy financing strategy and sustainable fisheries
In 2024, an assessment of the financial sector and Madagascar’s readiness for nature-related financial disclosures was also conducted.
Policy and Institutional Review (PIR). Although Madagascar’s sustainable development depends heavily on biodiversity, biodiversity considerations remain weakly integrated into national planning, sectoral policies, and the budget process. Stakeholders face limited human and financial resources, and the NBSAP is only partially implemented.
Biodiversity Expenditure Review (BER). Public spending on biodiversity conservation is low—under 3% of the national budget—and there is heavy reliance on donor funding, which is often irregular and unpredictable.
Financial Needs Assessment (FNA). The estimated financing required to implement the NBSAP over 2022–2025 is about US$900 million.
Biodiversity Finance Plan (BFP): 14 validated priority solutions
- Increase and improve the effectiveness of bi- and multilateral aid for biodiversity.
- Increase revenues from REDD+ by facilitating private-sector access to financing.
- Improve public budget execution through Results-Based Management (RBM).
- Operationalize Access and Benefit-Sharing (ABS), including a legal framework for bioprospecting.
- Pursue debt-for-nature swaps.
- Conduct a feasibility study on a conservation-agriculture subsidy to reduce deforestation.
- Develop a roadmap to access blue-carbon market opportunities.
- Mobilize additional resources to expand terrestrial and marine protected-area networks.
- Enable the National Forest Fund (FFN) to deploy earmarked forest revenues for sustainable forest management.
- Promote sustainable fishing (implementation of the Marine Spatial Planning, MSP, framework).
- Promote sustainable nature-based tourism.
- Promote natural capital accounting.
- Strengthen the legal framework for Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs), ERIPs, and biodiversity offsetting.
- Advance corporate social responsibility (CSR) in favor of biodiversity.
Support to the Ministry of Environment and Sustainable Development on Results-Based Budgeting (RBB).
Activities began with decentralized, in-person training across all regional directorates, involving ~150 planning and budgeting staff. Materials were redesigned to prioritize practical group exercises while providing essential theory. Sessions covered: a refresher on RBM, programme budgeting, principles and methods for developing a Medium-Term Expenditure Framework (MTEF) at the ministerial level, strategic planning, Priority Sectoral Action Plans (PASP), performance documents, and budgeting. Following the training and consultations, two ad hoc commissions were created in June 2025: the Monitoring and Evaluation System Commission and the MTEF Commission.
Readiness for nature-related financial disclosures.
Biodiversity loss could reduce Madagascar’s GDP by 4.2% by 2050, threatening forestry, fisheries, and tourism. In this context, nature-related financial disclosure aligned with the TNFD is essential to reconcile profitability with environmental stewardship. The financial system remains underdeveloped (no stock exchange and no specific green-lending framework), though initiatives such as green bonds are emerging. Financial authorities have not yet integrated biodiversity risks, and corporate reporting on nature impacts is rare, aside from compliance with international parent-company standards. The study underscores the importance of double materiality (companies’ impacts on nature and nature’s impacts on companies). While the current context does not yet support mandatory disclosure, momentum from BIOFIN and broader sustainable-finance initiatives provides a strong foundation. Recommended next steps include progressively establishing an adapted regulatory framework, strengthening institutional and private-sector capacity, and creating reliable environmental-data platforms.
Four financing solutions are currently being implemented:
Financing solution 1: Improve budget formulation and budget exécution procedures of the Ministry in charge of the environment at the central and regional levels through results-based budgeting (RBB) :
This support aims to strengthen the capacity of the Ministry in charge of the environment-appointed technicians involved in drawing up the Ministry's budget at the central and regional level, and in implementing it using results-based budgeting methodology.
Financing solution 2: Diversify and increase funding sources for institutions financing Protected Areas management:
The solution is being carried out with two local financial partners (FAPBM Biodiversity and Protected Areas Foundation and Tany Meva Foundation) and the main manager of Protected Areas in Madagascar (Madagascar National Park). This solution aims to diversify and increase the sources of funding for Madagascar's protected areas. The selected finance solutions include Biodiversity offsetting for FAPBM, capitalization of an endowment fund for Tany Meva, for community projects around Protected Areas, and impact investing/PPP for ecotourism for MNP
Financing solution 3: Mobilize financial resources to ensure sustainable management of forest resources:
The financing solution aims to mobilize additional financial resources for sustainable forest management by revising existing fees, royalties, fines, and penalties related to the forestry sector, improving their collection, and supporting the capitalization and operationalization of the National Forest Fund (FFN) currently being created.
Financing solution 4: Develop and implement a sustainable finance strategy for marine conservation and the sustainable use of coastal and marine resources in the blue economy:
The proposed financing solution aims to support the Malagasy new policy and institutional framework on blue economy (the National Blue Economy Strategy) by designing a sustainable financing strategy for biodiversity activities with climate change co-benefits, as outlined, and to prioritize and implement financing mechanisms that are expected to have a positive impact on nature or ensure the prevention of further loss of nature.
The PIR identifies national biodiversity vision, strategies and trends. In addition to showing that biodiversity remains poorly integrated into planning, sectoral policies and the national budgeting process, and that stakeholders generally have weak human and financial resources and the NBSAP is only partially implemented, the PIR identified/underlined:
- Twenty-four existing financing solutions for biodiversity.
- Subsidies harmful to biodiversity in the agricultural sector (e.g. taxes on agricultural inputs).
- The MEDD already has an important structure for biodiversity, which needs financial, technical and, above all, human resources to be effective.
- The MEDD cannot protect biodiversity on its own. Other sectors depend on and derive a large part of their benefits from biodiversity, and should therefore contribute.
- The development of a legal and institutional framework for private-sector involvement in biodiversity management and financing needs to be strengthened.
- Policies and laws for all sectors in Madagascar should explicitly consider the environment and biodiversity in their implementation.
- For protected areas, it is important to know the economic contribution of protected areas in Madagascar. This would enable additional financial resources to be mobilized, and a sustainable financing strategy for protected areas to be developed and implemented.
- The ecological compensation system will also be strengthened by developing a legal and institutional framework.
- Officials in the Ministry of Justice should be made aware of the economic importance of biodiversity for Madagascar, and their capacities should be strengthened in line with the international legal framework on biodiversity.
- In the agricultural sector, while the use of chemical inputs may seem indispensable in the short term, it is very important that the country can support farmers in optimizing their use and reducing their negative impact on biodiversity.
- Locally-managed marine areas in Madagascar must be supported and helped to finance their sustainable management.
- Public-sector spending on biodiversity conservation amounted to US$41.69 million over the 5-year study period. NGO and foundation spending, based on the sample taken, amounted to US$57.7 million. In short, biodiversity funding is dominated by environmental NGOs and foundations. This funding is heavily dependent on external sources.
- Government spending on investment is low (23%) compared with operating expenditure (77%). The involvement of other ministries in addition to the Environment and Agriculture ministries in incentive programs for biodiversity protection.
- The involvement of the private sector in financing biodiversity is important. We need to raise their awareness and knowledge of national and international obligations relating to the sustainable management and conservation of biodiversity and natural resources.
- The framework and implementation of environmental impact assessments must be strengthened.
- Develop partnerships between the private sector, civil society, local authorities and communities to implement management plans and facilitate the restoration of biodiversity, and finally facilitate the mobilization of financial resources for the private sector to implement nature-based solutions.
The aim of the Biodiversity Financial Needs Assessment (FNA) is to provide a comprehensive estimate of the financial resources required to achieve national biodiversity targets. These objectives are based on the NBSAP (2015 - 2025) and more precisely on the remaining period of the NBSAP, which runs from 2022 to 2025. The NBSAP is made up of 05 strategic axes and 20 Objectives.
To carry out this EBF, BIOFIN Madagascar drew up a logical framework for the NBSAP, classifying the activities proposed by various stakeholders (public sector, private sector and NGOs). Each activity was detailed, and one or more targets and key players were identified. Over 500 activities were identified during the data collection carried out by the NBSAP logframe consulting team.
The costs of implementing these activities were then estimated, and the activities were budgeted by determining their unit cost. Following this, it was possible to estimate the funding requirements for biodiversity conservation in Madagascar at 3.6 thousand billion Ariary, or just under 900 million USD for the period 2022-2025. In addition to the very substantial funding requirement, it was also identified that reforestation activities and the restoration and management of protected areas account for the bulk of NBSAP implementation costs.
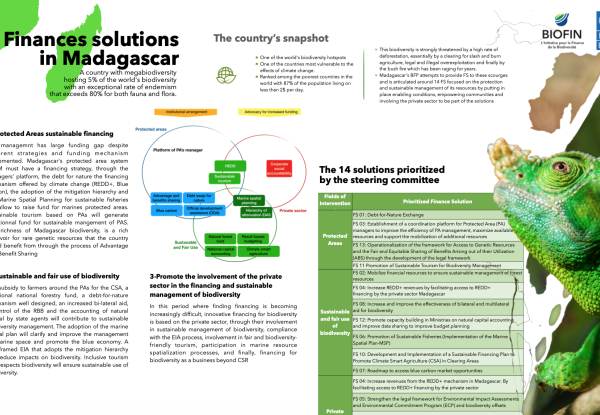
The Madagascar Biodiversity Financing Plan started with an identification of 85 used and potential financing solutions for Madagascar, and ended with 14 prioritized financing solutions for the sustainable management of Madagascar's biodiversity.
The 14 prioritized solutions are :
- SF 01: Debt-for-nature swap
- SF 02: Mobilize financial resources to ensure sustainable management of forest resources
- SF 03: Set up a coordination platform for Protected Area (PA) managers to improve the efficiency of PA management, maximize available resources and support the mobilization of additional resources.
- SF 04: Increase REDD+ revenues, by facilitating access to REDD+ financing by the private sector in Madagascar.
- SF 05: Strengthen the legal framework for Environmental Impact Assessments and Environmental Commitment Programs (PREE) and biodiversity offsetting
- SF 06: Promotion of sustainable fishing (application of the Marine Spatial Plan-MSP)
- SF 07: Roadmap to access blue carbon market opportunities
- SF 08: Increase and improve the effectiveness of bi- and multilateral aid for biodiversity
- SF 09: Improve public budget execution through results-based management (RBM)
- SF 10: Development and implementation of a sustainable financing plan to promote climate-smart agriculture (CSA) in land-clearing areas
- SF 11: Promote sustainable tourism for biodiversity management
- SF 12: Promote capacity building in Ministries on natural capital accounting and improve data sharing to enhance budget planning
- SF 13: Operationalize the framework for Access to Genetic Resources and Fair and Equitable Sharing of the Benefits Arising out of their Utilization (ABS) by developing the legal framework
- SF14: Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) in favor of Biodiversity